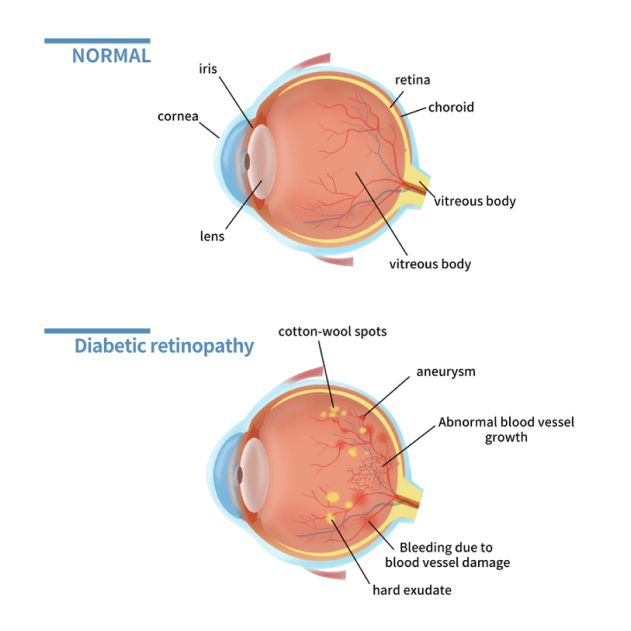
Diabetic Retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina. It is a complication of diabetes and is more likely to occur in individuals who have had diabetes for a long time or have poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, blood vessels in the retina may weaken and develop tiny bulges called microaneurysms. These microaneurysms can break causing small haemorrhages and swelling in the retina. When the swelling affects the central part of the retina called the macula, it is called diabetic macular oedema.
As the condition progresses, blood vessels can become blocked leading to reduced blood supply and triggering the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels. These vessels are fragile and bleed easily and can lead to large haemorrhages in the eye, scarring and even retinal detachment. This advanced form is called proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
In the early stage of diabetic retinopathy, you may not experience any symptoms. Regular diabetic eye examinations are essential for early detection and treatment, to prevent the risk of disease progression and severe vision loss.
As diabetic retinopathy progresses it will start to cause more noticeable problems including blurry vision, distortion, floaters, and patchy or sudden loss of vision.
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity and stage of the condition.
Early stages of diabetic retinopathy may not need treatment and your specialist may recommend close monitoring with regular eye examinations. To reduce the risk of disease progression it is important to control your blood sugar levels, follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take prescribed medications as directed.
For later stages of diabetic retinopathy, when vision is affected, treatment includes:
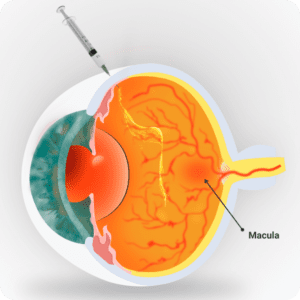
Intravitreal anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF is a medication that inhibits the growth of abnormal blood vessels and reduces leakage and swelling in the retina. The medication is injected into the affected eye into the vitreous cavity and is usually performed in the office under local anaesthetic drops.
For more information on Intravitreal injections please click here
Laser treatment
Laser treatment is used to seal off any leaking blood vessels, reduce swelling and inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth.
For more information on laser treatment please click here
Retinal surgery
In advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy where there is severe bleeding in the vitreous or scar tissue formation on the retina, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be necessary. During vitrectomy, the vitreous gel is removed and scar tissue is removed, allowing for better visual clarity.
For more information on vitrectomy please click here
Because the early stages of diabetic retinopathy can have no symptoms, it is crucial for all diabetic patients to have regular eye examinations for early diagnosis and treatment. Diabetic retinopathy is usually diagnosed during a comprehensive eye examination, this includes:
Dilated Eye Examination
This involves using eye drops to enlarge your pupils, which allows a better view of the retina at the back of your eye.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography
A non-invasive imaging scan that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina. It is mainly used to detect and monitor diabetic macular oedema.
Retinal Photography
Using a specialised wide-view camera that takes images of your retina to detect and monitor diabetic retinopathy
Fluorescein Angiography / Indocyanine Green Angiography
A diagnostic procedure used to examine the blood flow in the retina. It involves injecting a special dye called Fluorescein or ICG into a vein in your arm, then taking a series of photographs as the dye circulates through the blood vessels in the retina. The test identifies areas of leaking or abnormal blood vessels, blockages, swelling or other retinal conditions.
Copyright © 2023 Nexus Eye Care | Trans4m Business Consulting – Website Design & SEO | Privacy Policy | ^