What is Retinal Imaging?
Retinal imaging refers to the use of various specialised equipment to capture detailed images of the retina. These tests focus on the structure of the retina to; detect abnormalities, diagnose and monitor retinal disease.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography (OCTA)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to scan and capture detailed images of the eye. OCT functions similarly to ultrasound but utilises light waves instead of sound waves. It works by detecting and analysing the reflections of light within the tissue to generate high-resolution cross-sectional images.
OCT provides valuable information used to diagnose and monitor various eye conditions. It can be used to analyse different structures within the eye including:
Retinal imaging
This captures high-resolution images of the retina, allowing for detailed visualisation of its layers. This helps in the diagnosis and monitoring of conditions such as macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, macular holes and epiretinal membranes.
Anterior segment imaging
OCT can also image the front portion of the eye, including the cornea, iris, and lens. This is helpful in assessing conditions such as corneal abnormalities and angle-closure glaucoma.
OCT Angiography (OCTA)
OCTA is a specialised form of OCT that provides information about the blood flow within the retina and choroid without the need for dye injection. It aids in assessing blood supply to the macula in patients with diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusions as well as non-invasive visualisation of macular neovascularisation.
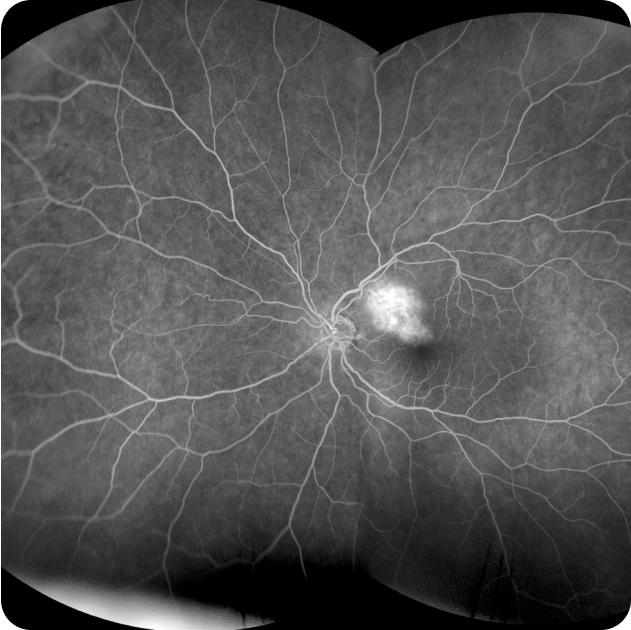
Fluorescein Angiography and Indocyanine Green (ICG) Angiography
Fluorescein Angiography and Indocyanine Angiography are diagnostic tests used to examine the blood flow in the retina. It involves injecting a special dye called Fluorescein or ICG into a vein in your arm, then taking a series of photographs as the dye circulates through the blood vessels in the retina. The test identifies areas of leaking or abnormal blood vessels, blockages, swelling, or other changes that may affect the health and function of the retina.
Fluorescein Angiography and Indocyanine Angiography are often used to diagnose and treat conditions such as:
- Macular Degeneration
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Macular Edema
- Retinal Vascular Disease
What is Ocular Ultrasound?
Ocular ultrasound, also referred to as ocular echography or B-scan is a non-invasive and painless test utilised in clinical settings to evaluate the structure of the eye and identify potential abnormalities. Similar to other ultrasound procedures, ocular ultrasound relies on the reflection of sound waves to generate detailed images of the eye’s internal structures, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Ocular ultrasound is recommended in specific situations where conventional eye examination is limited due to media opacities, these include:
- Suspected retinal detachment
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Ocular mass or tumours
- Inflammatory disease
- Dense cataracts or corneal opacities
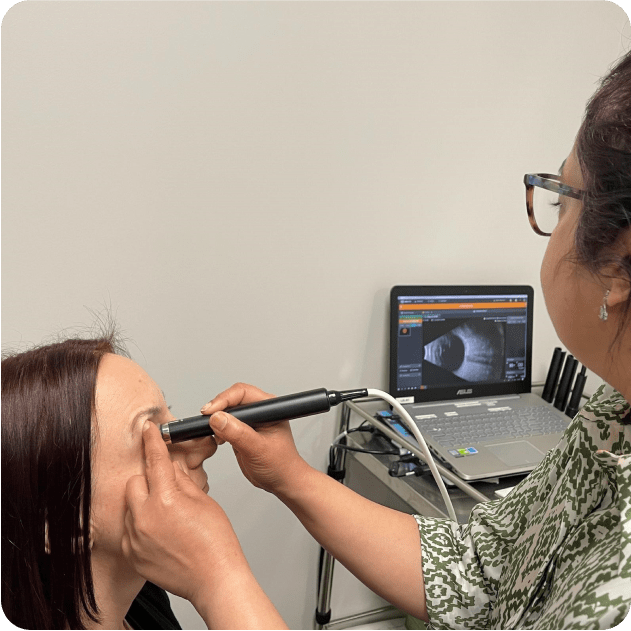
Wide view Retinal Photography and Autofluorescence
Wide-view retinal photography uses a specialized camera that takes images of your retina to detect and monitor macular and retinal conditions. In addition to macular pathologies, ultra-widefield retinal photography is particularly useful in the assessment of peripheral retinal pathologies and retinal tears. Autofluorescence is a special non-invasive imaging technique helpful in the detection of generalized retinal disorders such as retinal degeneration and dystrophies caused by genetic mutations.